Home > Teams > Advanced Core Facilities > HCEMM-SU In Vivo Imaging Advanced Core Facility
Head of ACF: Domokos Máthé DVM, Ph.D.
The In Vivo Imaging Advanced Core Facility provides services to
-all HCEMM Research Groups,
-HCEMM Member University-affiliated PIs
-and external academic or industrial parties, too.
We help you to cover the full range of quantitative data generated using most in vivo imaging modalities available nowadays.
We strive to include everything: from the generation of any live animal-related measurement ideas, through advice on contrast material use or metabolic imaging measurement types.
Our service extends to the development of radiomic outputs and statistical analysis of data.
Our constantly improving and quite comprehensive array of experience, animal model choices available, and imaging systems cover small rodents (CNS, tumour and stem cell use models) and large animals (dogs, swine) as well.
Use cases of the In Vivo Imaging ACF:
-Tg organism phenotyping via visualisation of reporter gene expression (e.g. -Luc,- mCherry, mKate)
-Cell knock-in or knock-out phenotyping using reporter gene approaches and measurement of cell tracking in live animals
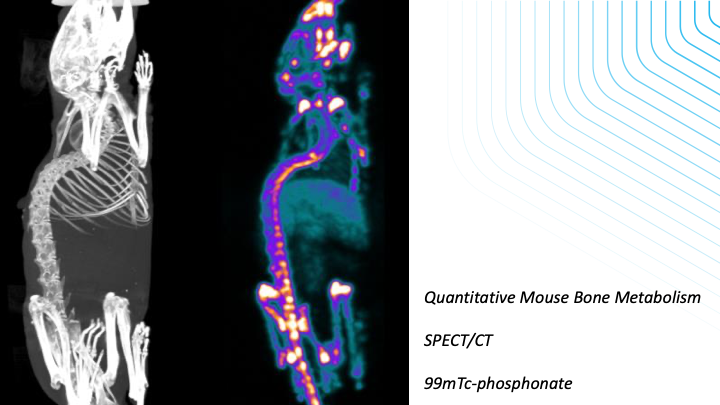
-Measurements of protein expression in quantitative manner using PET and SPECT
-Quantitative measurement of IC50 and Kd values for specific protein/antibody and receptor agonist/antagonist molecules using hybrid SPECT/MRI and PET/MRI imaging
-Efficacy measurements of drugs or cell-based therapies in CNS, bone/joint and tumour models using imaging readouts from fluorescence, SPECT, PET, MRI, CT or Ultrasound data
-Deciphering of CNS perfusion networks (fUS) and
-Tumour or inflammatory perfusion using ultra-high resolution ultrasound systems
-Proof-of-concept trials in large animal spontaneous disease (inflammatory bowel disease, lung fibrosis, and spontaneous tumours) by SPECT/PET/CT readouts
-Directly translational studies from the patient bed to bench and back to clinical trial: CAR-T cell therapy, radionuclide therapy and tumour radioembolisation
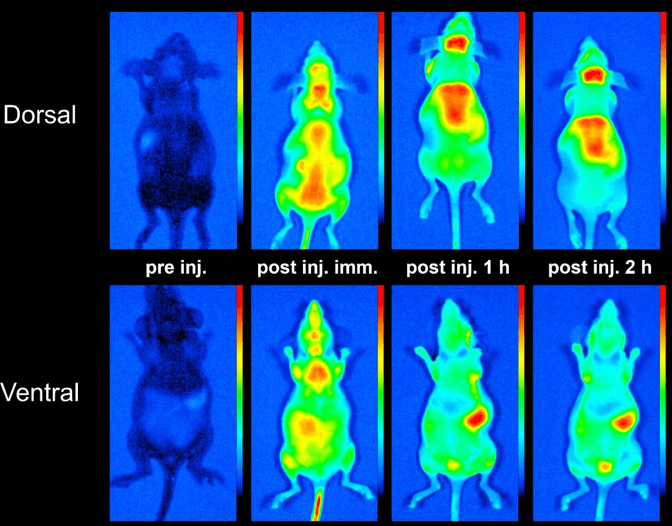
-Biodistribution measurements of fluorescent proteins/constructs, radiolabeling of proteins, quantitation of biodistribution with femtomol/g tissue sensitivity using PET and SPECT
Available Sites and Instrumentation:
The IVI ACF is located in three sites, the headquarters being the Basic Medical Sciences Building at the Semmelweis University, 37-43 Tűzoltó utca, 1094 Budapest. The ACF HQ comprises two isotope laboratories and three imaging laboratory rooms. Permissions are in place to handle more than 80 isotopes for tracing, imaging and therapeutics and X-ray application. In addition, a local isotope-containing animal facility is also associated with the ACF. Two other sites are also involved, the Cardiovascular Centre (68 Városmajor u, 1122 Budapest) and the Basic Sciences Centre (4 Nagyvárad tér, 1082).
Repertoire of Imaging Possibilities by Imaging Methods:
Rajmohamed Mohamed Asik, Natarajan Suganthy, Mohamed Asik Aarifa, Arvind Kumar, Krisztián Szigeti, Domokos Mathe, Balázs Gulyás, Govindaraju Archunan, Parasuraman Padmanabhan
Journal/Proc./Book: Biomedicines (9/9)
Year: 2021![]()
Zsófia Varga-Medveczky, Noémi Kovács, Melinda E. Tóth, Miklós Sántha, Ildikó Horváth, Luca Anna Bors, Katalin Fónagy, Timea Imre, Pál Szabó, Domokos Máthé, Franciska Erdő
Journal/Proc./Book: Frontiers in Neuroscience (15)
Year: 2021![]()
Parasuraman Padmanabhan, Mathangi Palanivel, Ajay Kumar, Domokos Máthé, George K. Radda, Kah-Leong Lim, Balázs Gulyás
Journal/Proc./Book: Emerging Topics in Life Sciences (4/6)
Year: 2020![]()
Mbuotidem Jeremiah Thomas, Enikő Major, Anett Benedek, Ildikó Horváth, Domokos Máthé, Ralf Bergmann, Attila Marcell Szász, Tibor Krenács, Zoltán Benyó
Journal/Proc./Book: Cancers (12/12)
Year: 2020![]()
László Forgách, Nikolett Hegedűs, Ildikó Horváth, Bálint Kiss, Noémi Kovács, Zoltán Varga, Géza Jakab, Tibor Kovács, Parasuraman Padmanabhan, Krisztián Szigeti, Domokos Máthé
Journal/Proc./Book: Nanomaterials (10/9)
Year: 2020![]()
Valeria Josa, Szilamer Ferenczi, Rita Szalai, Eniko Fuder, Daniel Kuti,
Krisztina Horvath, Nikolett Hegedus, Tibor Kovacs, Gergo Bagamery,
Balazs Juhasz, Zsuzsanna Winkler, Daniel S. Veres, Zsombor Zrubka,
Domokos Mathe, Zsolt Baranyai
Journal/Proc./Book: International Journal of Molecular Sciences (21/17)
Year: 2019![]()






